MOOKNAYAK MEDIA BUREAU | December 28, 2024 | Jaipur : In this article, we will cover one of the topics of this section i.e “Countries and their Capitals”. This is a very easy topic and if students read it comprehensively they will score good marks and the possibility of their selection will increase. In #SSC, #Banking, #LIC, #Railways, and other #competitive_exams, the General Awareness section plays an important role nowadays since it is a very scoring section.
Asian Countries with their Capitals and Population
Asia is the largest continent on Earth, both in size and population. It covers about 44.6 million square kilometers, which is nearly 30% of the planet’s land and 8.7% of its total surface area.

Separated from Europe by the Ural Mountains, Asia has been the cradle of the world’s earliest civilization and is home to around 60% of all people.
List of all countries and their capitals in Asia: In terms of its geographical location of Asia, Asia mainly lies in the northern and eastern parts of the world. It’s bordered by the Pacific Ocean in the east, the Indian Ocean in the south, and the Arctic Ocean in the north. Asia and Europe are part of the same landmass, connected through the Ural Mountains and across the Caspian Sea. Additionally, Asia links to Africa at the Isthmus of Suez.
Asian Countries List: Capitals of Asia
- Asia is the world’s most populous continent, home to more than 4.6 billion people. The most populous country in Asia is China with a population of 1.4 billion according to the US Census Bureau as of July 2021. China is also the most populous country in the world.2. More than 2,300 languages are spoken throughout the Asian continent. The most common of these is Mandarin Chinese, spoken by a whopping 51% of the entire population of Asia.
- The Asian elephant is smaller than African elephants, they have smaller ears and one more claw on each foot.
- India is the largest mango-producing country in the world with more than 20 million tons of mangoes produced each year.
- Of the top 10 rice-producing countries in the world, nine are in Asia i.e China, India, Indonesia, Bangladesh, Vietnam, Thailand, Myanmar, the Philippines, and Japan.
- The 100 highest mountains in the world are all on the Asian continent, with the highest being Mount Everest in the Himalayas of Nepal. Mount Everest, Nepal. Asia is home to the tallest mountains in the world.
- The most important religion in Asia is Islam with about 1.2 billion followers. In second place is Hinduism with about 900 million followers.8. Out of the 10 most populous cities in the world, seven are in Asia according to the 2021 World Population Revision.
- The word “Asia” is believed to be derived from the ancient Greek word “Aσία”. While the exact etymology is unknown, many believe the word means “sunrise” or “eastern light.
- Wild tigers used to live throughout the Asian continent, but today they can only be found in 13 countries on the continent: India, Nepal, Bhutan, Bangladesh, Myanmar, Russia, China, Thailand, Malaysia, Indonesia, Cambodia, Laos, and Vietnam. The Sumatran tiger is found in the jungles of Indonesia.
- The three countries with the highest life expectancy in the world are in Asia i.e Hong Kong, Japan and Macau.
- The smallest country in Asia is the Maldives.
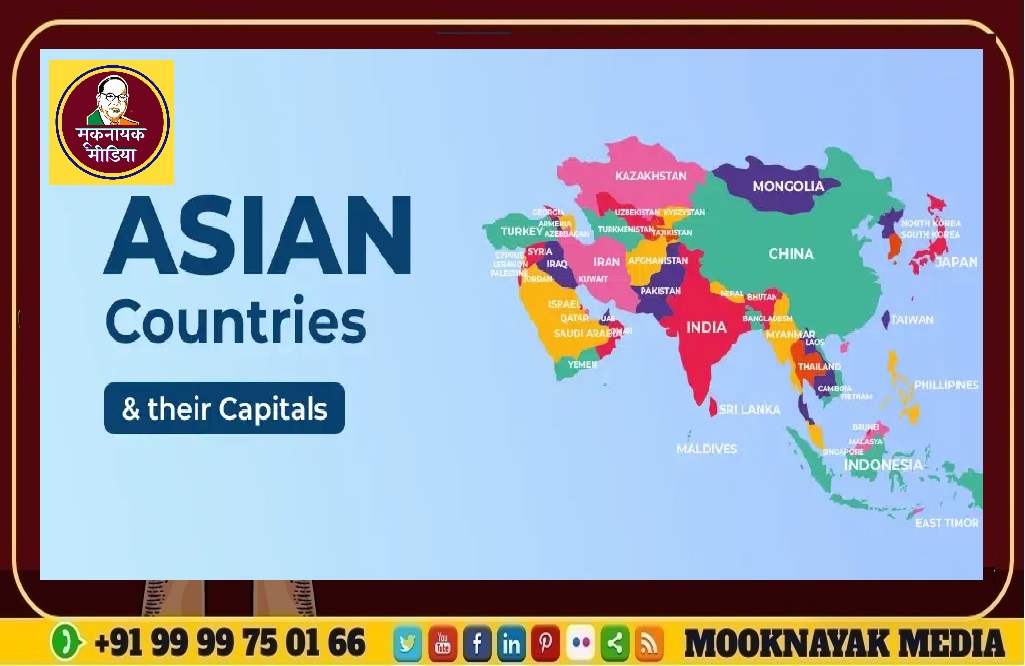
What are the 48 countries in Asia and their capitals
Asia, the largest continent on Earth, is a land of diversity, a rich tapestry of cultures and landscapes. It’s home to 48 unique countries, each with its own distinct capital city. Let’s begin on a journey to explore these nations and their capitals. It encompasses 48 unique countries, each with its own distinct capital city that serves as a window into the nation’s soul.
- China – Beijing: As the capital of the most populous country, Beijing is a bustling metropolis blending ancient history with modern development.
- India – New Delhi: New Delhi, the seat of government in India, is known for its wide boulevards and significant landmarks like the India Gate and Rashtrapati Bhavan.
- Indonesia – Jakarta: Jakarta, on the island of Java, is a vibrant hub of Indonesian culture, economy, and politics.
- Pakistan – Islamabad: Islamabad, known for its high standard of living and lush greenery, stands in contrast to the country’s more populous cities.
- Bangladesh – Dhaka: Dhaka, the capital of Bangladesh, is famous for its rich history and vibrant cultural scene.
- Japan – Tokyo: Tokyo, a city that never sleeps, is a blend of cutting-edge technology and timeless traditions.
- Philippines – Manila: Manila, the heart of the Philippines, is a densely populated bayside city with a history spanning centuries.
- Vietnam – Hanoi: Hanoi, known for its centuries-old architecture, is a symbol of Vietnam’s complex history.
- Turkey – Ankara: Ankara, the capital of Turkey, sits in the country’s central Anatolia region and is a center for commercial and industrial activities.
- Iran – Tehran: Tehran, set against the backdrop of the Alborz mountains, is a bustling metropolis and the political and economic heart of Iran.
- Thailand – Bangkok: Bangkok is famous for its ornate shrines and vibrant street life, reflecting Thailand’s unique culture.
- Myanmar – Naypyidaw: Naypyidaw, a city purpose-built to be the capital, is known for its wide boulevards and monumental architecture.
- South Korea – Seoul: Seoul, a city that melds history with technology, is the heartbeat of South Korea.
- Iraq – Baghdad: Baghdad, once a significant center of the Islamic Golden Age, is steeped in history.
- Afghanistan – Kabul: Kabul, set in a narrow valley, has been an important strategic location throughout history.
- Saudi Arabia – Riyadh: Riyadh, a desert metropolis, is the political and administrative center of Saudi Arabia.
- Uzbekistan – Tashkent: Tashkent, known for its many museums, is a testament to Uzbekistan’s rich history.
- Malaysia – Kuala Lumpur: Kuala Lumpur, characterized by its famous Petronas Towers, is a symbol of Malaysia’s rapid development.
- Yemen – Sana’a: Sana’a, one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world, is the historical heart of Yemen.
- Nepal – Kathmandu: Kathmandu, nestled in the Himalayan foothills, is known for its historic temples and vibrant culture.
- Sri Lanka – Colombo: Colombo, a bustling port city, is a blend of colonial heritage and modern vibrancy, reflecting Sri Lanka’s rich history.
- Cambodia – Phnom Penh: Phnom Penh, situated at the confluence of rivers, is known for its historical and cultural significance in Cambodia.
- Laos – Vientiane: Vientiane, a city with a laid-back charm, is famous for its French colonial architecture and Buddhist temples.
- Mongolia – Ulaanbaatar: Ulaanbaatar, the coldest capital city in the world, is a unique blend of traditional Mongolian culture and urban development.
- Nepal – Kathmandu: Kathmandu, set against the backdrop of the Himalayas, is renowned for its historic temples and vibrant street life.
- Oman – Muscat: Muscat, known for its dazzling souks and superb seafood, is the picturesque capital of Oman.
- Qatar – Doha: Doha, a city known for its futuristic skyscrapers and ultramodern architecture, is the economic center of Qatar.
- Syria – Damascus: Damascus, one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world, is rich in history and culture.
- United Arab Emirates – Abu Dhabi: Abu Dhabi, a city of opulent mosques and beautiful waterfronts, is the modern and wealthy capital of the UAE.
- Jordan – Amman: Amman, a city of contrasts blending the ancient and the modern, is the cultural and political hub of Jordan.
- Lebanon – Beirut: Beirut, often referred to as the ‘Paris of the Middle East’, is known for its vibrant nightlife and rich history.
- Kyrgyzstan – Bishkek: Bishkek, set against the backdrop of the Tien Shan mountains, is known for its wide boulevards and Soviet-era architecture.
- Tajikistan – Dushanbe: Dushanbe, meaning ‘Monday’ in Tajik, is a city with lush green parks and Soviet-era buildings.
- Turkmenistan – Ashgabat: Ashgabat, known for its white marble buildings and grandiose national monuments, is the heart of Turkmenistan.
- Uzbekistan – Tashkent: Tashkent, a city with a mix of modern and Soviet-era architecture, is the cultural and economic center of Uzbekistan.
- Kazakhstan – Nur-Sultan: Nur-Sultan, formerly known as Astana, is a symbol of Kazakhstan’s rapid modernization with its futuristic skyline.
- Armenia – Yerevan: Yerevan, one of the world’s oldest continuously inhabited cities, is known for its Soviet-era architecture and vibrant cultural scene.
- Azerbaijan – Baku: Baku, a city famed for its medieval walled old city, is the cosmopolitan capital of Azerbaijan.
- Georgia – Tbilisi: Tbilisi is known for its diverse architecture and mazelike, cobblestone streets.
- Bhutan – Thimphu: Thimphu, a city that uniquely blends traditional Bhutanese culture with modernity, is the intriguing capital of Bhutan.
- Brunei – Bandar Seri Begawan: Bandar Seri Begawan, known for its opulent mosque and serene water village, is the peaceful capital of Brunei.
- Maldives – Malé: Malé, a densely populated island city, is the commercial and political center of the Maldives.
- Singapore – Singapore: Singapore, a global financial center, is a bustling city-state known for its multicultural population and green spaces.
- East Timor (Timor-Leste) – Dili: Dili, set along the coast, is known for its historic Portuguese influence and significant role in East Timor’s history.
- Palestine – East Jerusalem: East Jerusalem, a city of great religious significance, is the proclaimed capital of Palestine.
- Yemen – Sana’a: Sana’a, one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world, is known for its unique architecture and historical significance.
- Cyprus – Nicosia: Nicosia, the world’s last divided capital, is rich in history and culture, with a blend of Greek and Turkish influences.
- Israel – Jerusalem: Jerusalem, a city of profound religious significance to Jews, Christians, and Muslims, is the proclaimed capital of Israel.
Each of these capitals offers a glimpse into the diverse tapestry of Asia, showcasing a blend of ancient traditions, cultural richness, and modern development. From the bustling streets of Singapore to the historic alleys of Jerusalem, these cities are not just administrative centers but the heart and soul of their respective countries.
Must Read : Asia has around 2300 languages and nearly 5 billion people
Ranking Of Asian Countries By Population
Geographically, the countries in Asia are categorized into six distinct regions. These regions are Northern Asia, Western Asia, Central Asia, Eastern Asia, Southern Asia, and Southeast Asia. Below, you’ll find a list of Asian countries, along with their respective populations.
| Rank | Country | Population | Remarkable Fact |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | China | 1.4 billion | World’s longest continuous civilization. |
| 2 | India | 1.3 billion | World’s largest democracy. |
| 3 | Indonesia | 273 million | World’s largest island country. |
| 4 | Pakistan | 220 million | Home to the second-highest mountain, K2. |
| 5 | Bangladesh | 163 million | Known for its lush greenery and waterways. |
| 6 | Japan | 126 million | Land of the rising sun and advanced technology. |
| 7 | Philippines | 109 million | Known for its stunning beaches and biodiversity. |
| 8 | Vietnam | 97 million | Famous for its rich history and cuisine. |
| 9 | Turkey | 84 million | A transcontinental country in Eurasia. |
| 10 | Iran | 83 million | Rich in cultural heritage and history. |
Kindly Donate to ‘Mooknayak Media’ For Magnify Birsa Ambedkar Phule Fatima Mission